Software solutions with microservices architecture
Mar 13, 2025
Flexibility and scalability for the production of the future
In today's manufacturing industry, companies face the challenge of designing their production processes to be both efficient and flexible to remain competitive. Modern software solutions like Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) and Manufacturing Operations Management (MOM) play a central role in this. The architecture of these systems significantly influences their performance and adaptability. While MES solutions have traditionally been built as monolithic systems, MOM solutions are increasingly adopting a microservices architecture. This article explores the differences between monolithic and microservices architectures and highlights the advantages of microservices in manufacturing.
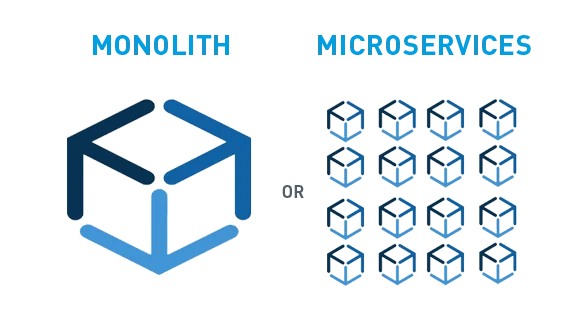
Monolithic Architecture (MES) vs. Microservices (MOM)
The Monolith architecture is akin to a single, large block of stone – solid, uniform, and unyielding. In this traditional framework, a single process encapsulates all functional elements of the software application. Imagine it as a large container where all the features, such as user interface components, business logic, data access code, and more, are tightly interwoven and deployed as one unit. The monolithic approach has its advantages, such as straightforward development and deployment processes since everything is bundled together. However, it also presents significant challenges when it comes to scaling, as any small change requires the entire application to be updated and redeployed. This can lead to longer downtime and more complex updating procedures, which can be a hindrance in fast-paced manufacturing environments where flexibility and quick adaptation are key.
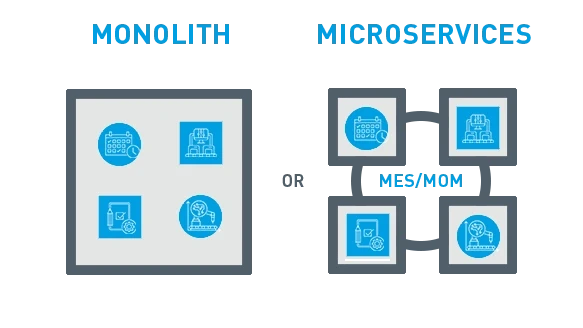
In contrast, Microservices architecture is presented as a collection of smaller, modular processes, likened to a set of interlocking building blocks. Each microservice is independent and focuses on a specific business function, communicating with other services through well-defined interfaces. This structure offers a more flexible and scalable approach, as each microservice can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently of the others. This modular setup aligns well with MOM systems, where different manufacturing processes might require rapid and specific adjustments without disrupting the entire system. It enables continuous delivery and deployment practices that are essential for modern manufacturing operations seeking agility and efficiency.
When comparing the two architectures side by side, as depicted in the graph, it becomes evident that the flexibility, scalability, and independence of microservices offer a more adaptable and resilient framework. This is particularly beneficial for manufacturers looking to innovate and stay competitive, as it allows for faster implementation of new features, easier maintenance, and more robust security measures.
Advantages of microservices architecture
- Flexibility: Each microservice can be developed and operated independently, allowing for easy addition or modification of new functions. This gives companies the ability to respond quickly to market changes.
- Scalability: Unlike monolithic systems, microservices can be scaled individually. Companies can expand only the services that require more resources without adjusting the entire system.
- Simple Integration: Microservices are based on open interfaces like APIs, making them easy to integrate into other systems. This simplifies connectivity to existing enterprise solutions such as ERP or SCM.
- Autonomous Data Management: Each microservice can store and process its data, minimizing the risk of system failures. A failure in one service does not affect the entire application.
- On-Premises and Cloud: MOM solutions based on microservices can be operated both on-premises and in the cloud, providing companies with additional flexibility in implementing their software solutions.
Practical examples
A classic example of the benefits of microservices architecture in MOM systems is the seamless integration of production data from different machines. Specialized microservices can collect production data from SMT interfaces or other machines and consolidate it in a central system. This enables comprehensive analysis and optimization of manufacturing processes in real time.
- Data Integration: Microservices process data from various sources and facilitate integration into the production system.
- Configuration Management: Microservices offer extensive configuration options, allowing companies to customize and optimize their production processes.
Customer-centric benefits
Microservices architecture is instrumental in delivering improved customer experiences by enabling faster response times, greater customization, and innovation in product offerings. With the ability to develop and deploy microservices independently, manufacturers can quickly adapt to customer needs and market demands. This agility allows for the continuous enhancement of products and services, ensuring that companies remain competitive. Furthermore, the modular nature of microservices supports personalized solutions, enabling businesses to offer tailored experiences that resonate with their customers. As a result, microservices not only enhance operational efficiency but also drive customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Security considerations
While microservices architecture offers numerous advantages, it also presents unique security challenges that require attention. The decentralized nature of microservices means that secure APIs and robust data protection measures are critical to safeguarding sensitive information. Each microservice must be secured to prevent vulnerabilities across the network. Implementing a comprehensive security strategy that includes encryption, authentication, authorization and continuous monitoring is essential to protect the integrity of manufacturing operations. By addressing these security considerations, companies can confidently adopt microservices while mitigating potential risks.
Challenges of microservices
Microservices architecture also presents certain challenges that companies must navigate. One of the primary challenges is the increased complexity associated with managing a distributed system. Unlike monolithic architectures, where all components are housed within a single application, microservices require coordination and communication across multiple independent services. This can lead to complexities in service orchestration, monitoring, and troubleshooting.
Additionally, microservices often necessitate additional resource requirements due to the redundancy of data and communication. Each microservice may need to maintain its own data store, leading to potential data duplication and increased storage needs. Furthermore, the communication between services, typically through APIs, can introduce latency and require robust network infrastructure to ensure seamless operation.
Addressing these challenges requires a strategic approach, including the implementation of effective monitoring tools, robust security measures, and efficient resource management practices. By acknowledging and preparing for these potential hurdles, companies can fully leverage the advantages of microservices while maintaining operational efficiency and reliability.
In summary
Transitioning from a monolithic architecture to a microservices architecture offers significant benefits, including increased flexibility, scalability, and maintainability. Solutions like the iTAC.MOM.Suite exemplify how microservices can enhance production efficiency and adaptability in response to market changes.
However, it's important to recognize and address the challenges that come with this transition, such as increased complexity and additional resource requirements. Implementing strategic solutions, including robust security and efficient resource management, will enable organisations to fully benefit from microservices. In an increasingly digital and interconnected world, microservices remain a pivotal component of a future-proof manufacturing environment, driving innovation while ensuring operational reliability and efficiency.